What are Anchored Retaining Walls?
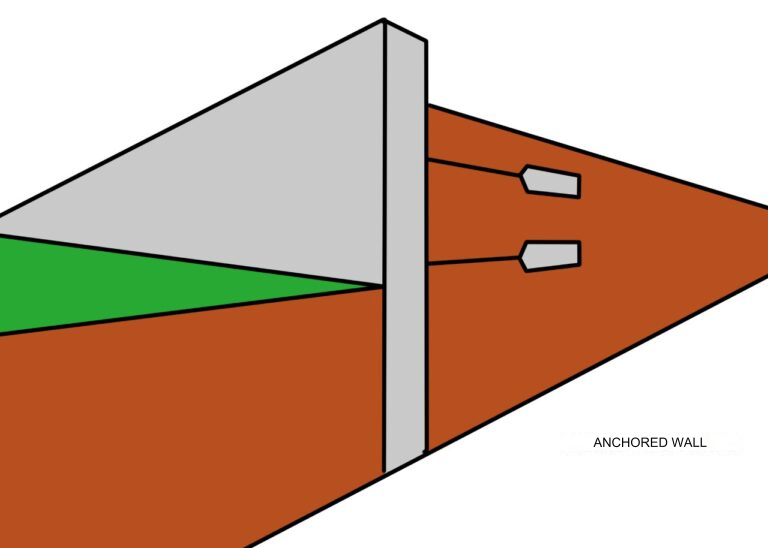
Anchored retaining walls are engineered structures designed to withstand forces generated by soil pressure, preventing the soil from shifting or collapsing. These walls are constructed using a combination of vertical elements, such as concrete or masonry walls, and anchors extending into the soil behind the wall.
Anchors are typically high-strength bars or cables connected to the retaining structure and inserted into the soil at an angle. The tension exerted by these anchors helps counteract the forces pushing the soil against the wall, providing stability and preventing collapse.
Functioning of Anchored Retaining Walls
Understanding how anchored retaining walls function is a critical aspect to comprehend how these structures can resist soil forces and maintain stability in challenging terrains. Below, we will delve into the details of their operation:
Retaining Wall: The retaining wall is the visible part of the structure and is located at the front of the system. It can be constructed using various materials such as concrete, masonry, treated wood, or even prefabricated segments. The retaining wall is designed to resist soil pressure, which tends to push it forward. The key to its operation lies in its ability to effectively distribute and resist these forces.
Anchors: Anchors are the hidden and essential part of anchored retaining walls. They consist of high-strength bars or cables, usually made of steel, extending from the top of the wall into the soil behind it. These anchors are installed at a specific angle relative to the wall and penetrate the soil to a depth depending on the terrain conditions.
Tension and Compression: The operation of anchored retaining walls is based on two opposing forces: tension and compression. When the retaining wall bears the soil pressure tending to push it forward, the anchors are tensioned. This tension in the anchors counteracts the soil force, preventing the wall from shifting or collapsing. In other words, the anchors act as “rescue cables” preventing the wall from yielding under soil pressure.
Soil Resistance: The effective functioning of anchored retaining walls also depends significantly on soil resistance. Before designing and installing these walls, a geotechnical study must be conducted to understand the soil characteristics at the specific location. This involves determining the soil resistance and its capacity to withstand the tension exerted by the anchors. Based on this information, suitable anchors are selected, and the installation depth is determined.
Global Stability: The system’s operation is a delicate balance between the tension generated by the anchors and the compression exerted by the soil against the wall. When this balance is maintained, the overall stability of the structure is achieved. If the soil pressure exceeds the anchors’ resistance, the anchored retaining wall may yield. Therefore, precise design and installation are crucial to ensuring effective operation.
Maintenance and Monitoring: It is important to note that over time, soil conditions may change due to factors such as weather conditions and erosion. Therefore, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure that anchored retaining walls continue to function effectively. This may involve inspecting anchors, repairing potential damages, and reviewing soil resistance at regular intervals.
Factors When Choosing Anchored Retaining Walls
The choice of a type of retaining wall, whether an anchored retaining wall or another type, depends on various factors that must be carefully considered. Here are some of the factors taken into account when selecting an anchored retaining wall over another type:
Soil Type: The soil type at the project location is a critical factor. Anchored retaining walls are effective in a variety of soils, but a geotechnical study must be conducted to determine soil resistance and characteristics. Other types of retaining walls may be more suitable for specific soils.
Wall Height: The required retaining wall height is an important factor. Anchored retaining walls are suitable for moderate to high heights. For lower heights, other types of walls, such as gravity walls or masonry walls, may be considered.
Available Space: Site space availability influences the choice of retaining wall type. Anchored retaining walls are often used in urban areas where space is limited, as they allow for optimal use of available land.
Design Load: The load that the retaining wall must bear is a critical factor. Anchored retaining walls can resist significant loads due to their anchors, making them suitable for projects requiring high load capacity.
Costs and Budget: The project budget is a determining factor in choosing the type of retaining wall. Anchored retaining walls are often more cost-effective compared to other types of walls in certain situations. However, a cost analysis is essential to determine the most economical option.
Aesthetics and Architectural Design: In some projects, aesthetics and architectural design are important considerations. Anchored retaining walls may be less aesthetically pleasing compared to other types of walls, so this factor may influence the choice.
Environmental Conditions: The climatic and environmental conditions of the area must also be considered. In coastal or areas prone to extreme weather, anchored retaining walls may be a favorable option due to their durability and resistance.
Local Regulations and Standards: Local regulations and construction standards can affect the choice of retaining wall type. It is important to ensure that the selected wall type complies with all local regulations and requirements.
Project Timelines: Project timelines are a crucial factor. Some types of retaining walls may require longer construction times than others. Anchored retaining walls are usually quick to install, which can be advantageous in projects with tight timelines.
How Widely Used Are Anchored Retaining Walls?
The demand for anchored retaining walls has been steadily increasing in recent decades due to their versatility, effectiveness, and efficiency in a wide variety of applications. Let’s delve into the prevalence and relevance of these retention systems:
Wide Application: Anchored retaining walls are used in a broad range of applications, from slope stabilization and road protection to the construction of underground infrastructure and landslide prevention. This versatility has contributed to their widespread use in different industries.
Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to other retention structures, anchored retaining walls are often a more cost-effective option. This makes them attractive for projects with budget constraints, driving their use in many regions.
Durability and Long Lifespan: When designed and constructed correctly, anchored retaining walls are durable and require minimal maintenance. This durability makes them a long-term investment, motivating government entities and businesses to choose this option.
Flexibility in Different Terrains: Anchored retaining walls adapt to a wide variety of environments and soil types. They are ideal for areas with varied and challenging terrains, contributing to their use in construction projects worldwide.
High Demand in Urban Areas: In densely populated urban areas, where space is limited and valuable, these walls allow for maximizing available land by creating underground parking areas, terraced gardens, and constructing buildings on steep slopes.
Landslide Prevention: In regions prone to landslides, anchored retaining walls are an effective solution for stabilizing slopes and reducing the risk of disasters. Their ability to prevent property damage and save lives has led to their widespread use in these areas.
Applications in Mining and Quarrying Industry: In the mining and quarrying industry, where slope stability is crucial for worker safety and safe.





Related
Gravity Retaining Walls
Methods for Paver Calculation – Civil Engineering
All About Reinforced Concrete – Construction