The Bright Future of Renewable Energies: Sustainability and Advances in Engineering
Humanity finds itself at a critical juncture in its history. Growing awareness of the depletion of natural resources and the harmful effects of climate change has led us to seek sustainable solutions for our energy needs. In this context, renewable energies have emerged as a fundamental pillar of modern engineering and a beacon of hope for a cleaner and more sustainable future.
What Are Renewable Energies?
Renewable energies, also known as clean or sustainable energies, are energy sources obtained from natural sources that constantly renew over time and do not deplete on human scales. Unlike fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas, and coal, whose extraction and consumption have a significant environmental impact and are finite, renewable energies represent a more sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to meet our energy needs. The main sources of renewable energy include solar, wind, hydroelectric, geothermal, and biomass.
1. Solar Energy: The Light that Illuminates Our Future
Solar energy is one of the most well-known and widely used renewable energy sources worldwide. It harnesses solar radiation reaching the Earth and converts it into electricity or heat through solar panels. Advances in solar cell technology have significantly improved the efficiency and affordability of this energy source, driving its widespread adoption.
In the case of photovoltaic solar systems, solar cells are used to convert solar light directly into electricity, while solar thermal heating systems capture solar energy to heat water or thermal fluids used in heating and cooling applications.
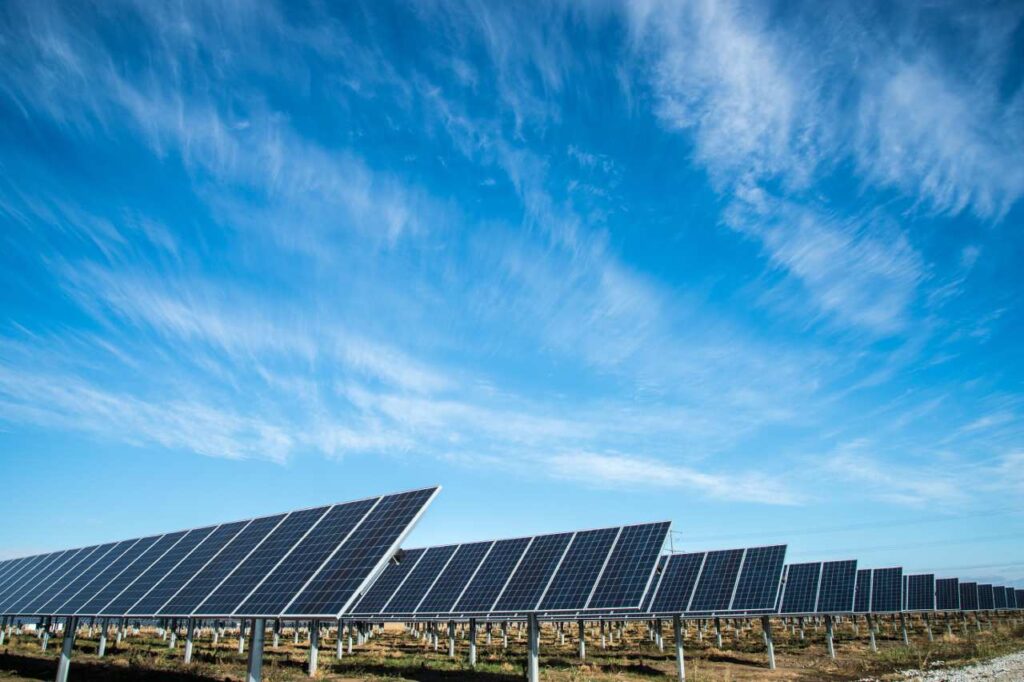

2. Wind Energy: The Power of the Wind
Wind energy is derived from the wind, which drives the blades of wind turbines, converting the kinetic energy of the wind into electricity. The strategic placement of wind farms in areas with consistent winds has maximized their efficiency and contribution to the global energy matrix, such as mountain slopes, coasts, or open areas. This renewable energy source has experienced impressive growth in recent decades and has become a significant source of energy generation in various countries. Offshore wind energy, developed at sea, is also gaining popularity due to its potential to generate large amounts of energy.

3. Hydroelectric: The Force of Moving Water
Hydroelectric energy is one of the oldest and most widely used renewable energy sources worldwide. This energy source harnesses the flow of water, typically through dams and turbines, to generate electricity. Dams can store water in reservoirs and release it as needed for electricity demand, allowing for efficient control of generation. Hydroelectric power plants can generate large amounts of electricity and offer a constant and reliable source of energy, although their environmental and social impact may be subject to debate in some cases.

4. Geothermal: Earth's Energy
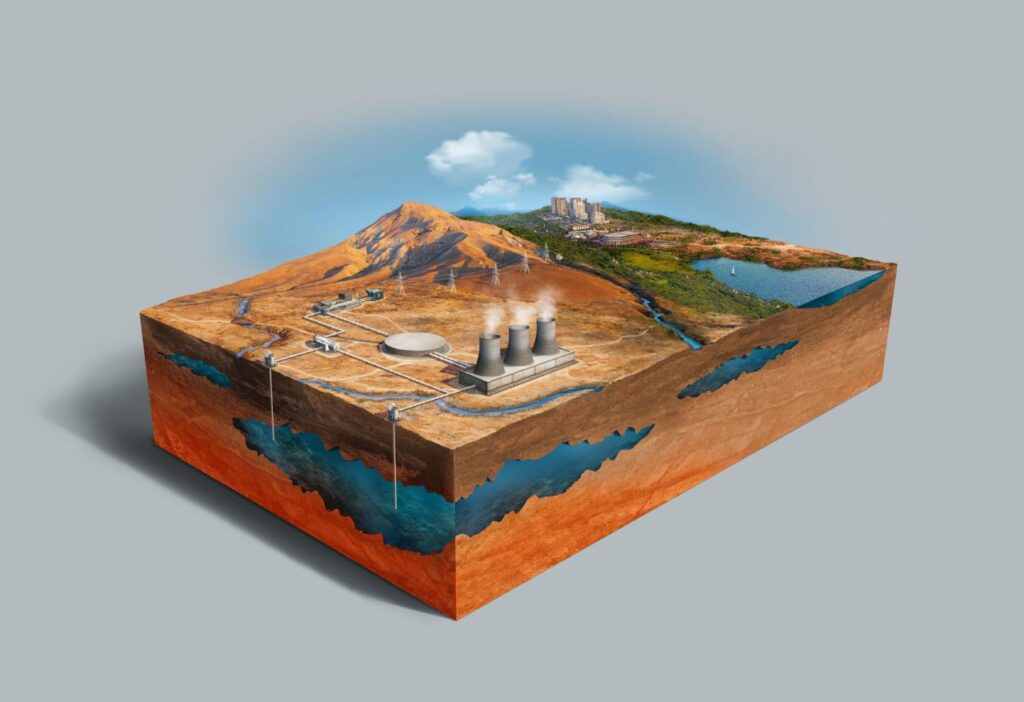
Geothermal energy harnesses the natural heat from the Earth’s interior. It is based on the principle that as you go deeper into the Earth, the temperature increases. Geothermal systems use geothermal heat pumps to transfer this heat to buildings for heating and cooling purposes. In addition, binary cycle geothermal plants harness the temperature difference between underground hot water and surface cold water to generate electricity. Geothermally active areas, such as Iceland and the Pacific Ring of Fire, are particularly suitable for geothermal energy generation.

5. Biomass: Turning Waste into Energy
Biomass refers to any organic material that can be used as an energy source. This includes wood, agricultural residues, food waste, and other biodegradable materials. Biomass energy is obtained by burning these materials to generate heat or electricity. It is also used to produce biofuels like biodiesel and ethanol, which are mixed with fossil fuels to reduce emissions. Additionally, biomass is used in residential heating systems and in power plants that generate electricity from the burning of solid waste.

Characteristics of Renewable Energies:
Environmental Sustainability: Renewable energies are characterized by their inherent environmental sustainability. This is because they rely on natural sources that constantly renew, such as solar radiation, wind, biomass, and terrestrial heat. Unlike non-renewable resources like oil and coal, which deplete over time, renewable sources are virtually inexhaustible on a human scale. This feature is essential to ensure a long-term energy supply without depleting Earth’s finite natural resources.
Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions: One of the standout features of renewable energies is their ability to generate energy with minimal or zero emissions of greenhouse gases. During energy generation from renewable sources like solar, wind, or hydroelectric power, significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) or other atmospheric pollutants are not released. This significantly contributes to mitigating climate change by reducing emissions of heat-trapping gases in the atmosphere, which cause global warming.
Diversity of Sources: Another key characteristic of renewable energies is the diversity of available sources. Each type of renewable energy has its own applications and advantages depending on geographic and climatic conditions. For example, solar energy is ideal for regions with high sun exposure, while wind energy is more effective in areas with consistent winds. Biomass is a viable option in places with abundant residual biomass, such as agricultural or forestry waste. This diversity allows for adaptation to the specific energy needs of different regions and communities.
Evolving Technology: Renewable energies are a field of constant technological evolution. Advances in engineering and research enable improvements in energy capture and conversion efficiency while reducing associated costs. For example, the efficiency of photovoltaic solar panels has increased significantly in recent decades, and modern wind turbines are more efficient and require less maintenance. This technological evolution not only enhances the economic viability of renewable energies but also promotes innovation and competitiveness in the engineering sector.
Low Environmental Impact: Compared to conventional energy sources, renewable energies often have a much lower environmental impact. The construction and operation of renewable energy plants tend to generate less air and water pollution and generally occupy less space compared to coal mines or oil wells. Furthermore, renewable energy facilities can be designed and managed to minimize the impact on local wildlife and flora.
Advantages of Renewable Energies:
Reduced Dependence on Fossil Fuels: One of the most obvious advantages of renewable energies is that they reduce dependence on fossil fuels like oil and coal. This not only reduces vulnerability to price fluctuations in the energy market but also contributes to a country’s energy security.
Job Creation: The transition to renewable energies creates a significant number of jobs in the engineering sector, from equipment manufacturing to the installation and maintenance of renewable energy systems.
Human Health Benefits: Reducing emissions of air pollutants associated with burning fossil fuels improves air quality and has a positive impact on public health. Fewer respiratory diseases and less harm to health are additional benefits.
Price Stability: Unlike fossil fuels, whose prices can be volatile, many forms of renewable energy have more predictable and stable operating costs, helping to stabilize electricity prices.
Importance of Renewable Energies:
Mitigating Climate Change: Renewable energies play a critical role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By generating electricity and heat with minimal or no CO2 emissions, they help limit global warming and meet international commitments, such as the Paris Agreement. This is essential to avoid the catastrophic impacts of climate change, such as rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss.
Energy Security: Dependence on fossil fuels, often from geopolitically unstable regions, poses risks to the energy security of countries. Renewable energies diversify the energy source, reducing vulnerability to disruptions in the supply of oil or natural gas. This increases the stability and resilience of the energy infrastructure.
Long-Term Sustainability: Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are virtually inexhaustible on a human scale. Unlike fossil fuels, which deplete over time, renewable energies can supply energy sustainably for decades and even centuries. This ensures a stable and predictable energy supply in the long term.
Reduction of Air and Water Pollution: Energy generation from fossil fuels results in the release of pollutants that affect air and water quality, with severe consequences for human health and the environment. Renewable energies, by not emitting these pollutants, contribute to improving air quality and conserving water resources.
Job Creation and Economic Development: The transition to renewable energies creates jobs in the clean energy industry, from manufacturing and installing equipment to research and technology development. Additionally, investment in renewable energies stimulates economic growth by boosting the demand for related services and products.
Access to Energy in Underserved Communities: Renewable energies can be particularly important in remote or developing regions where there is no access to traditional energy sources. Decentralized solar, wind, or hydroelectric systems can provide clean and reliable energy to communities that would otherwise be excluded from the benefits of electricity.
Promotion of Technological Innovation: Research and development in renewable energies drive innovation in engineering and technology. These advancements not only improve the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of renewable energies but also have applications in other fields, such as energy storage and sustainable mobility.
In summary, renewable energies are an essential part of the solution to the world’s most pressing global issues, including climate change, energy security, and improving the quality of life. Their significance lies in their ability to provide a sustainable, clean, and versatile energy source that benefits both the environment and society at large. Their adoption and continued development are crucial for a safer, more prosperous, and more sustainable future.
Renewable Energies as a Bet on the Future
Renewable energies emerge as an undeniable bet for the future in a world seeking sustainable solutions to energy and environmental challenges. They represent the promise of an endless and clean energy source, essential for mitigating climate change and ensuring energy security. As technology advances, these energy sources become increasingly efficient and economically viable. Moreover, they drive job creation, foster innovation in engineering, and promote nations’ energy independence. Renewable energies are not only an urgent necessity but also an exciting opportunity to transform the way we generate and consume energy, paving the way for a cleaner, more sustainable, and prosperous future for future generations.
Clean energy has become a fundamental pillar in the fight against climate change. Its ability to generate electricity and heat with minimal emissions of greenhouse gases is essential to reduce humanity’s carbon footprint. By choosing sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy, we are reducing our dependence on highly polluting fossil fuels. This shift toward a cleaner energy mix not only contributes to slowing global warming but also opens the door.
What is the energy of the future?
Solar energy clearly emerges as the energy source of the future. With constant advancements in solar panel efficiency and energy storage capacity, solar energy is gaining ground as the most promising and versatile energy source. Harnessing abundant and virtually unlimited solar radiation.
Solar energy is not only clean and sustainable but can also be deployed on a small or large scale, from residential installations to large solar farms. Its potential to reduce carbon emissions, boost energy independence, and create jobs in the engineering field makes it an undeniable frontrunner.
Conclusion
Undoubtedly, renewable energies have emerged as an imperative response to the environmental and energy challenges facing our planet in the 21st century. In summary, the clearest and most encouraging conclusion is that these energy sources represent a path to a more sustainable future. As awareness of climate change and the limitation of fossil resources grows, renewable energies stand out as an unparalleled solution. Their ability to generate clean and renewable electricity, whether through solar panels capturing solar energy, wind turbines harnessing the power of the wind, or hydroelectric plants channeling the energy of water, is essential for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and decreasing our reliance on fossil fuels. Furthermore, the expansion of these technologies creates jobs in the clean energy sector and promotes innovation in energy efficiency.
In the end, the clearest conclusion is that investing in renewable energies is not only a sensible choice to preserve our planet but also an investment in a healthier and more prosperous future for future generations.





Related
Sustainable Construction: Lean Construction Philosophy
Internet of Things in Civil Engineering