A brief introduction to this engineering field.
Electrical Engineering is an exciting branch of engineering dedicated to the study and application of the principles of electricity, electromagnetism, and electronics to design, develop, and optimize systems and devices that use electrical energy. This discipline plays an essential role in modern society, as it is responsible for providing the energy that powers our lives and driving technological innovations that transform our daily interactions.
What is Electrical Engineering?
Electrical Engineering encompasses a vast field that focuses on the generation, transmission, distribution, and utilization of electrical energy. Essentially, electrical engineers work with electrical current and circuits to provide technical solutions that drive the economy, industry, communications, and the general well-being of humanity.
Key Areas of Specialization
Within Electrical Engineering, there are various areas of specialization that allow engineers to focus on specific fields based on their interests and skills. Some of the primary specialties include:
- Electronics and Microelectronics: This branch focuses on the design and development of small-scale electronic devices and integrated circuits. Engineers in this specialization work on creating key components, such as transistors, diodes, and microprocessors, which form the foundation of modern technology, from smartphones to vehicle navigation systems.
- Power Systems: Electrical engineers who specialize in power systems are involved in the study and design of large-scale electrical systems, such as power generation plants, transmission networks, and distribution systems. Their goal is to ensure efficient and safe transmission of electrical energy from generation sources to end consumers.
- Control and Automation: This specialty focuses on the development of control and automation systems for various devices and processes. Electrical engineers in this area work on designing algorithms and systems that enable task automation and the monitoring of industrial processes, such as industrial robots and flight control systems, among others.
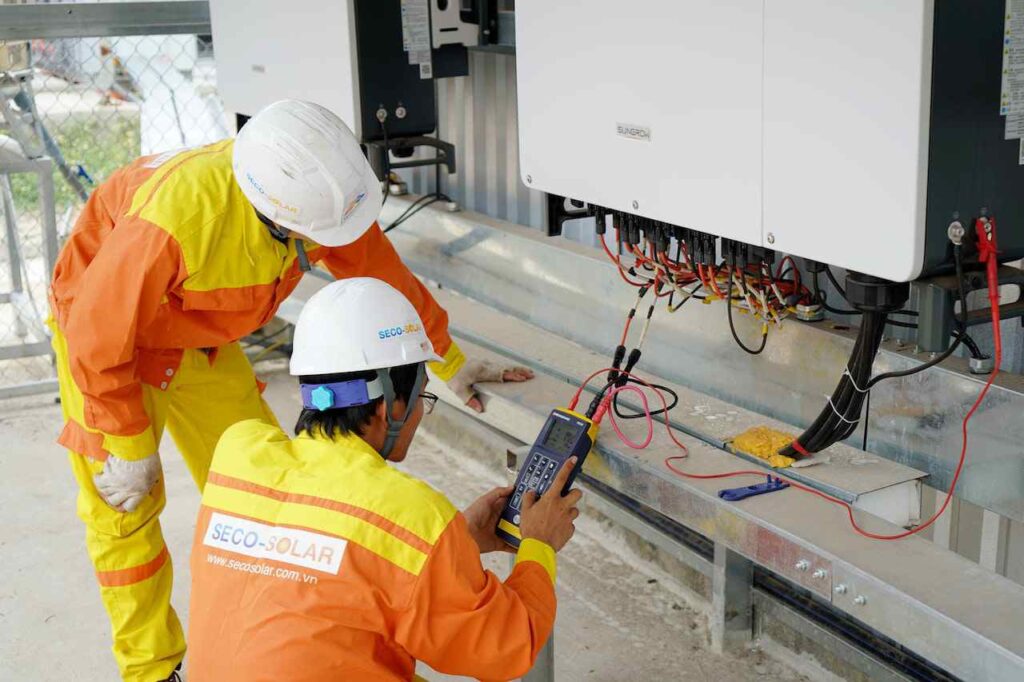

What Exclusive Electrical Engineering Subjects Do Its Students Face?
When an undergraduate student embarks on the exciting journey of Electrical Engineering, they will encounter various subjects that lay the foundations for their future career. Here are three exclusive subjects that are typically part of the undergraduate curriculum in Electrical Engineering:
- Electromagnetic Theory: This subject is fundamental for any Electrical Engineering student. It delves into the fundamental laws governing the behavior of electric and magnetic fields, providing the theoretical basis for understanding how electrical devices and systems function. In this subject, students will learn about Maxwell’s equations, electromagnetic wave propagation, and how to calculate electric and magnetic fields in different scenarios.
- Electric Circuits: In this course, students will immerse themselves in the world of electric and electronic circuits. They will learn about fundamental laws such as Ohm’s Law and techniques for analyzing and designing circuits in direct current and alternating current. In addition, they will be introduced to basic electronic components and learn how to build functional circuits.
- Analog and Digital Electronics: This subject introduces students to the exciting world of electronics. In its analog part, it covers circuits that work with continuous signals, such as amplifiers and filters. On the other hand, in the digital part, students will explore the fundamentals of digital electronics, including logic gates, sequential circuits, and more complex digital systems.
Professional Profile of an Electrical Engineer
A student of Electrical Engineering develops a versatile and multidisciplinary professional profile that makes them true leaders in the fields of engineering and technology. During their academic training, they acquire a deep understanding of the fundamental principles of electricity, electromagnetism, electronics, and power systems. This theoretical foundation is complemented by practical skills in the design and analysis of electrical and electronic systems, using cutting-edge tools for simulation and prototype development.
The electrical engineer is a natural problem solver, capable of tackling complex challenges and finding innovative solutions. They possess an analytical and critical mind, enabling them to approach situations from different perspectives and make informed decisions. The ability to work in a team is a key characteristic in this profession, as most electrical engineering projects require collaboration from multiple disciplines to achieve success.
Furthermore, the electrical engineer must be a lifelong learner, as the field of electrical engineering is constantly evolving due to technological advancements and changing societal demands. The ability to adapt and stay updated with the latest trends and developments in their field is essential for long-term professional success.
Roles and Areas of Work of an Electrical Engineer
Electrical engineers have a wide range of employment opportunities in various industries, thanks to their specialized knowledge and technical skills. Some of the most common positions that an electrical engineer can hold include:
- Electronic Design Engineer: In this role, the electrical engineer is responsible for designing electronic circuits and systems for various applications, such as medical devices, communication equipment, control systems, and more.
- Power Systems Engineer: This role involves working on the generation, transmission, and distribution of electrical energy, ensuring efficient and safe delivery to end users.
- Control and Automation Engineer: Electrical engineers who specialize in this field focus on designing and developing computer-controlled and automated systems, such as industrial robots and automated production systems.
- Research and Development Engineer: In this area, electrical engineers participate in research and development projects to create new technologies, improve existing products, and explore innovative solutions.
Regarding work areas, electrical engineers can work in different types of companies, such as:
– In the Energy Industry: Working in power generation, transmission, and distribution companies, contributing to efficient and sustainable electricity supply.
– Electronics and Telecommunications Industry: Participating in the creation of electronic devices, communication systems, and consumer electronics products.
– Automotive Industry: Collaborating in the design of electrical and electronic systems for electric vehicles and automotive control systems.
– Technology and Consulting Companies: Providing consulting services in the design and optimization of electrical and electronic systems.
Conclusion
Electrical Engineering is a fascinating discipline that encompasses everything from the manipulation of small electrical currents to the management of complex power distribution networks. With specialties ranging from electronics and microelectronics to power systems and automatic control, electrical engineers are at the forefront of technological innovation driving the modern world. Through fundamental and exclusive subjects, undergraduate students acquire the skills and knowledge necessary to face the challenges of tomorrow in this exciting engineering field.
A Motivational Message for Future Electrical Engineering Students
To the young individuals considering embarking on the exciting career of Electrical Engineering, I want to convey that you have chosen a passionate profession full of opportunities to make a significant difference in the world. Electrical energy is at the heart of modern society, and as electrical engineers, you will be the drivers of innovation and technological progress.
Throughout your education, you will face challenges and moments of uncertainty, but these experiences will be your greatest sources of learning and growth. Learn to embrace challenges as opportunities to improve and enhance your skills. Never underestimate your potential, and always strive for excellence in everything you do.
Remember that electrical engineering has the power to transform the world. From designing sustainable energy systems to creating electronic devices that improve people’s quality of life, your efforts will have a significant impact on society and the future of humanity.
Maintain your curiosity and passion for learning because knowledge is the foundation of innovation. Electrical engineering is a constantly evolving field, and your willingness to continue learning and adapting to new technologies and challenges will set you apart and lead the way toward a brighter future.
Finally, never underestimate the power of teamwork. Collaborating with other professionals and sharing ideas will allow you to reach more creative and effective solutions. Engineering is a collective effort, and by working together, you can tackle complex challenges and achieve ambitious goals.
So, young electrical engineers, prepare for an exciting and rewarding journey. Your dedication and passion for this career will make you leaders in technological advancement and agents of change for a better world. The future is in your hands, and electrical engineering is the path to reach it! Move forward and succeed on your path to knowledge and innovation!
See also Electrical Engineering and Mechatronics Engineering.
References
- Fundamentos de la Ingeniería Eléctrica por William D. Smart
- Ingeniería Eléctrica por John W. Nilsson y Stephen R. Riedel
- Ingeniería Eléctrica por Donald A. McQuarrie
- Ingeniería Eléctrica por Charles K. Alexander y Matthew N. O. Sadiku
- Ingeniería Eléctrica por Steven M. Burns
Artículos y sitios web
- IEEE Spectrum
- EE Times
- Electronic Engineering Times
- Electronic Design
- Digi-Key Electronics
About The Author
Samuel Parariá
Estudio: University of Francisco de Paula Santander.
Major: Civil Engineering.
Favorite Areas: Structures, Traffic Engineering, and Road Design.
Location: Cúcuta, Norte de Santander, Colombia.





Related
Do you want to study Aerospace Engineering? – Discover what it is.
What does a Chemical Engineer do?
What is Industrial Engineering?