The Colors of Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a field of study in science that utilizes living organisms or parts of them to develop products and processes with diverse applications in society. In its early days, it was categorized into four main areas, identified by colors: red, white, green, and blue. These categories represented specific applications of biotechnology in industry and science. However, with the remarkable increase in diversity and scope over time, it became necessary to expand this classification from four to eleven categories. This growth in application variety reflects the increasing importance and versatility of biotechnology in fields ranging from medicine to agriculture and environmental conservation.
Here are the 11 colors of biotechnology:
1) Red Biotechnology or Medical Biotechnology
Red Biotechnology, or medical biotechnology, focuses on applying biological techniques and principles to improve human health. This discipline has become highly relevant and promising in medicine and healthcare. Its diverse applications are fundamental to addressing diseases, developing innovative therapies, and improving people’s quality of life. One notable application is gene therapy, introducing healthy genes into the body to correct or replace defective genes causing genetic diseases. Tissue engineering is another exciting area seeking to create artificial tissues and organs or regenerate damaged tissues using living cells and biological matrices. Additionally, red biotechnology plays a crucial role in developing biotechnological drugs, such as recombinant proteins and monoclonal antibodies, essential in treating various diseases.
2) Blue Biotechnology (Marine Biotechnology)
Blue Biotechnology, or marine biotechnology, focuses on studying and applying marine organisms and resources for various purposes. It encompasses areas such as marine biodiversity, aquaculture, marine product biotechnology, bioprospecting, and marine conservation. This discipline leverages marine organisms and their biotechnological products to develop innovative solutions in fields from food to scientific research and conservation. Blue biotechnology contributes to improved aquaculture, extraction of bioactive compounds for pharmaceutical and nutritional applications, and the conservation of threatened species and sustainable management of marine ecosystems.
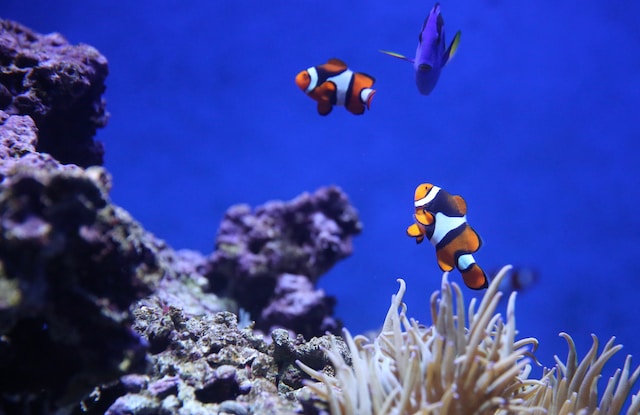

3) Green Biotechnology (Agriculture, Plants, and Fertilizers)
Green biotechnology focuses on applying biotechnological techniques to improve agriculture and food production. This includes genetically modifying plants to confer beneficial characteristics such as pest resistance, improved nutritional quality, and environmental sustainability. Through plant genetic engineering and the creation of transgenic crops, the aim is to promote more productive and efficient agriculture, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and fertilizers. Green biotechnology contributes to the conservation of genetic resources and the promotion of sustainable agricultural practices, playing a fundamental role in food security and mitigating the environmental impact of agriculture.

4) White Biotechnology
White biotechnology, or industrial biotechnology, focuses on applying biotechnological processes and techniques in industry to produce a wide range of chemicals, materials, and energy more sustainably and efficiently. By intelligently using microorganisms and biological processes, this branch of biotechnology contributes to reducing dependence on finite resources such as oil, simultaneously decreasing environmental impact. White biotechnology excels in areas such as producing bioplastics from renewable sources, bioremediation of contaminated soils and waters, generating sustainable biofuels, and treating wastewater, thus promoting more sustainable and environmentally friendly industrial practices.

5) Yellow Biotechnology
Yellow biotechnology, also known as food biotechnology, focuses on applying biotechnological techniques and processes to improve the production, quality, and safety of the foods we consume. Through genetic modification of plants and animals, microbial fermentation in food production, and the development of more efficient preservation methods, this branch of biotechnology plays a fundamental role in enhancing the food chain. Yellow biotechnology also contributes to the detection and prevention of foodborne diseases and the production of enzymes that improve the texture and quality of food products. In summary, yellow biotechnology works to provide us with safer, more nutritious, and tastier foods while addressing crucial challenges in food safety and sustainability.

6) Brown Biotechnology
Brown biotechnology, often linked to animal welfare, focuses on applying biotechnological techniques and approaches to improve the living conditions, health, and well-being of animals, both in livestock production and the conservation of endangered species. In agricultural and livestock production, this branch of biotechnology works on the genetic improvement of animals to reduce stress and diseases, increase food production efficiency, and promote more humane practices in animal breeding and management. In biodiversity conservation, brown biotechnology is employed in preserving endangered species. This includes assisted reproduction techniques such as in vitro fertilization, embryo transfer, and cloning to increase the population of threatened species and ultimately aid in their survival. Additionally, genetic marking techniques are used to track and study animal populations in the wild, essential for their conservation.

7) Purple Biotechnology
Purple biotechnology, also known as legal or ethical biotechnology, plays a crucial role in analyzing and managing legal, ethical, and institutional aspects related to the development and application of biotechnology. This branch of biotechnology focuses on addressing fundamental issues surrounding biotechnological innovation, from the research of biological materials, which may include microorganisms, plants, animals, and humans. Purple biotechnology ensures that advances in biotechnology develop within a robust legal and ethical framework, balancing innovation with the protection of society and the environment. Furthermore, it promotes ongoing dialogue among scientists, lawmakers, the medical community, and society at large to make informed and ethical decisions in the field of biotechnology. This discipline plays a vital role in shaping public policies and regulations that influence the development and application of new biotechnological technologies.

8) Golden Biotechnology
Golden biotechnology refers to the application of genetic engineering and bioinformatics to enhance the nutritional value and beneficial characteristics of agricultural crops. This technology focuses on the genetic modification of plants to address public health issues, such as vitamin A deficiency, by creating crop varieties that contain essential nutrients for the human diet.

9) Gray Biotechnology
Gray biotechnology is a constantly evolving field that significantly influences our daily lives by addressing environmental problems through biology and genetics-based technological solutions. It focuses on solving environmental problems, with varied applications addressing challenges such as soil and water pollution, purification of exhaust gases and other pollutants, as well as waste and residual substance recycling.

10) Orange Biotechnology
Orange biotechnology is a branch of biotechnology that focuses on education, outreach, and training in the field of biotechnology. Its main goal is to disseminate and facilitate the understanding of biotechnological concepts in society at large. To achieve this, orange biotechnology provides interdisciplinary information and training, addressing biotechnological topics from various perspectives, including biology, chemistry, and ethics.

11) Black Biotechnology
Black biotechnology focuses on the research and control of microorganisms and substances that could be used for harmful purposes. Its goal is to enhance security and preparedness in the face of potential biological threats, as well as to better understand the biology of these elements with applications in preventing and responding to biological emergencies. Black biotechnology focuses on the prevention, detection, and response to biological threats, contributing to the safety and preparedness for possible emergency situations.

In biotechnology, its scope is diverse, and each branch seeks specific solutions and advancements in its respective fields. Biotechnology has revolutionized many industries and continues to play a crucial role in improving the quality of life and sustainability worldwide.






Related
What is green biotechnology? – The Engineer
What is Red Biotechnology?